Bleeding Gums: 9 Major Causes and Remedies
Summarize with AI
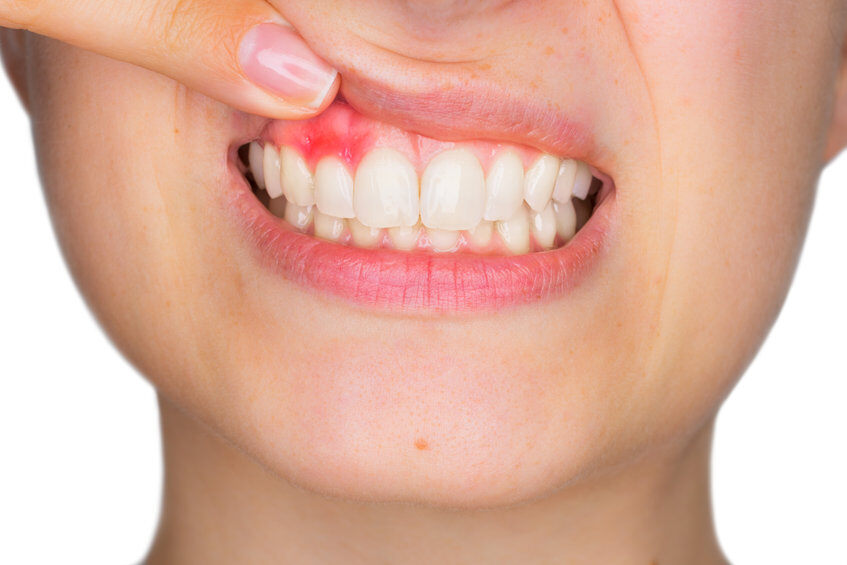
Bleeding gums can cause significant stress, especially if you don't know why it's happening. If you have noticed that your gums are bleeding, here’s what you should know.
What Causes Gums to Bleed?
Bleeding gums can cause significant stress, especially if you don’t know why it’s happening. Gums can bleed for a variety of reasons and many times the causes are not serious. However, bleeding can also point toward larger issues that may require extensive dental treatment if not caught early. The most common causes of gum bleeding include:
1. Medications:
Since they can thin the blood and reduce its ability to clot, certain types of medications can promote bleeding gums. This is one big reason it's especially important to tell your dentist about every supplement and medication you are taking, especially before you get any type of dental treatment.
2. Gingivitis:
The first stage of periodontal disease, gingivitis occurs when plaque causes gums to become inflamed. When this happens, the tissue may become tender and swollen. Many times, bleeding will occur when you eat, brush or floss. You can reduce your risk of gingivitis by maintaining good brushing and flossing habits. You should also get regular dental checkups to learn how to prevent gingivitis, and catch any minor issues before they develop into full-fledged gum disease.
3. Flossing:
Ideally, you should not bleed while flossing. That said, if you are just beginning a new flossing routine, your gums may not be used to the physical contact. You can minimize bleeding by using a gentle technique during the first few days. If, however, your gums continue to bleed after a week of routine flossing, you should visit your dentist to see if the bleeding is occurring due to an underlying problem with your teeth or gums.
4. Your toothbrush:
If you switch from a soft-bristled toothbrush to one with firm bristles, your gums could take a while to adjust. Until they do, you may experience mild bleeding. Again, if this continues for longer than a few days, visit your dentist to check for underlying issues. You should also consider switching back to a soft-bristled toothbrush.
5. Pregnancy gingivitis:
Sometimes, pregnant women will experience bleeding and swollen gums when they brush. Known as pregnancy gingivitis, this occurs due to hormonal changes that affect the way the body responds to oral bacteria. While it can be unnerving, pregnancy gingivitis should clear up once you are no longer expecting. That said, it's important to maintain regular exams during your pregnancy to make sure your bleeding isn't caused by periodontal disease.
6. Poorly-fitted dentures:
When dentures don't fit well, they can cause gums to bleed. If your dentures feel too big, too small or move around in your mouth, visit your dentist.
7. Medical issues:
In some instances, a person's gums will bleed in response to an underlying health issue, such as diabetes, heart disease, leukemia or vitamin deficiencies. If your dentist rules out common causes of gum bleeding, he or she may recommend that you visit your physician to test for potential health problems that may affect the way your blood clots.
8. Tobacco products:
If you smoke or use chewing tobacco, your gums are more likely to bleed. You are also at an increased risk of periodontal disease and oral cancer.
9. Sores or lesions:
Canker sores or cancerous lesions can also cause gums to bleed. Your dentist will check for these types of problems, when he or she is examining your mouth.
Treatment for Bleeding Gums
The best way to prevent your gums from bleeding is to maintain good oral hygiene. This means brushing at least two times per day and flossing at least once per day. If your bleeding is caused by excessive plaque buildup, you will need to get a professional cleaning from a qualified dental hygienist.
If your bleeding is owed to gum disease, your dentist will need to use more aggressive treatment strategies, such as root planing or scaling, which can slow down gum disease. If you have advanced periodontal disease, your dentist may suggest periodontal therapy or other treatments. In severe cases, surgery may be required to stop bleeding gums.
.png)

